

The principle of classical conditioning in which one can differentiate between two stimuli i.e. Greater the similarity, greater is the effect. Although the effect is not as intense as the original one but it helps a lot. we stop at the red traffic lights without bringing their shape or size in consideration. When in a gathering, he sees people smoking, he feels as if he is smoking.Ī phenomenon in which the stimuli, similar to the conditioned stimulus, starts generating the same response as that generated by conditioned stimulus is called stimulus generalization e.g. Another example is that of a person who has quitted smoking. Pavlov observed that after extinction, when the bell started ringing, the dog salivated at the ring only despite the fact that he did not give any meat to the dog after ringing the bell. This phenomenon is called extinction of a response.Ī principle or stage of classical conditioning in which a conditioned response, which has been extinguished earlier, reemerges after a long break is called spontaneous recovery e.g. it was observed in Pavlov experiment that when ringing bell (conditioned stimulus) was presented without meat (unconditioned stimulus) repeatedly, the response (salivation) started decreasing and eventually it disappeared. If we present conditioned stimulus without the unconditioned stimulus multiple times, the conditioned response starts decreasing till it disappears e.g. in Pavlov experiment ,the time till the dog starts salivation at ring of bell can be called as the stage of acquisition. This is the initial stage of learning in which responses are established and then strengthened as a result of repeated presentations or experiments e.g. The stage or principle of classical conditioning in which the stimulus under observation starts generating a response similar to the unconditioned response is called Acquisition.

The stages or principles of classical conditioning are acquisition, extinction, Spontaneous recovery, stimulus generalization and Stimulus discrimination.
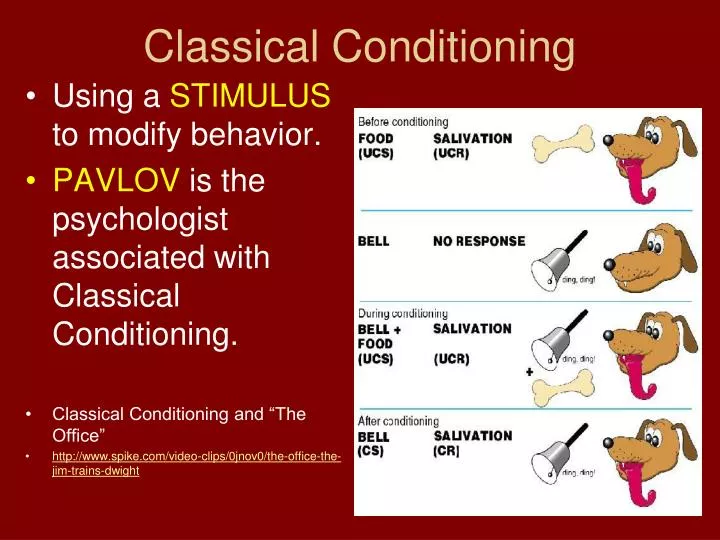
Principles/Stages of Classical Conditioning: But when rat (NS) was presented repeatedly after being paired with noise, the appearance of rats also started generating the same response (fear) as that generated by the noise i.e. He used to give a Fear (UCR) response to Noise (UCS). In this experiment, a small baby called Albert’s behavior was observed. In other words, we can say that neutral stimulus (ringing bell) has become a conditioned stimulus.Īnother experiment to study the concept of classical conditioning is called Little Albert Experiment. But when the experiment was repeated for multiple days, he observed that the dog salivated (conditioned response) at the ring only. In the initial days, the dog salivated at food only. He used to ring a bell (neutral stimulus) and then give food (unconditioned stimulus) to the dog under observation. He attached a tube with the salivary gland of a dog to measure the amount of saliva. Ivan Pavlov performed an experiment to explain the phenomenon of classical conditioning. Conditioned Response is a response similar to unconditioned response but is generated by the conditioned stimulus e.g.Unconditioned Response is a naturally generated response of unconditioned stimulus e.g.Conditioned Stimulus, a previously neutral stimulus, starts generating a response similar to that generated by unconditioned stimulus after being paired with an unconditioned stimulus e.g.Unconditioned Stimulus is that which brings about a response naturally e.g.Neutral stimulus is a stimulus which does not generate any response before conditioning e.g.Classical Conditioning:Ī type of learning in which a neutral stimulus, when paired with an unconditioned stimulus, starts generating the same response as that generated naturally by an unconditioned stimulus and becomes conditioned is called classical conditioning.Ī type of learning in which an organism starts giving a particular response to that stimulus, to which it does not give that response in daily routine is called classical conditioning.
/2794863-operant-conditioning-a21-5b242abe8e1b6e0036fafff6.png)
The scholarship allows level programm(s) in the field of taught at. Classical Conditioning & its Principles is open for.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
